There are several types of paraphrasing, each with its own purpose and approach. Paraphrasing enables us to reword a text or idea in our own words while preserving the original meaning. Learn more about reword meaning and the definition of paraphrasing.
What are the different Types of paraphrasing?
1. Word-for-Word Paraphrasing:
This type of paraphrasing involves rephrasing a sentence or passage while maintaining the original sentence structure and meaning. It’s often used when you need to clarify or simplify a complex idea without changing the wording significantly.
Here are some examples of Word-for-Word Paraphrasing:
Original Sentence: “The invention of the internet revolutionized communication.”
Paraphrased version: “The emergence of the internet brought about a significant transformation in how people communicate.”
2. Sentence Rewriting:
Sentence rewriting, often referred to as rephrasing, focuses on changing the structure of a sentence while retaining its original meaning. This technique is valuable for avoiding plagiarism and enhancing readability.
Consider this example:
Original Sentence: “She won the marathon, and her achievement made her hometown proud.”
Rewritten version: “Her victory in the marathon filled her hometown with pride due to her remarkable accomplishment.”
3. Summarizing:
Summarizing involves condensing a longer text into a shorter version while retaining the main points and key ideas. It’s a common way to create concise versions of lengthy documents or articles.
Take a look at this summary:
Original Text (longer passage): “In the 20th century, numerous technological innovations changed the world. These advancements included the development of computers, the internet, and the discovery of antibiotics. These breakthroughs had profound impacts on society, from the way people work and communicate to the treatment of diseases.”
Summarized version : “The 20th century witnessed transformative technological innovations, such as computers, the internet, and antibiotics, which reshaped various aspects of society, including work, communication, and healthcare.”
4. Paraphrasing:
In this type of paraphrasing, you restate the ideas or concepts presented in the original text using your own words. This can help you understand and explain complex ideas more clearly. For example:
Original: “The theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of the universe.”
Output: “The concept of relativity transformed how we perceive the cosmos.”
5. Reordering:
Sometimes, you may need to rearrange the order of words, phrases, or sentences within a text while maintaining the overall meaning. This can help improve the flow and coherence of your writing.
Here’s an example:
Original: “Despite his lack of experience, he quickly adapted to the new job.”
Reordered sentence version: “He quickly adapted to the new job, despite his lack of experience.”
6. Rewording:
This type of paraphrasing involves replacing words or phrases in the original text with synonyms or words with similar meanings. It’s a straightforward way to avoid using the same words as the original while conveying the same message.
If you need assistance with this paraphrasing type, consider using our free rewording tool to simplify the process.
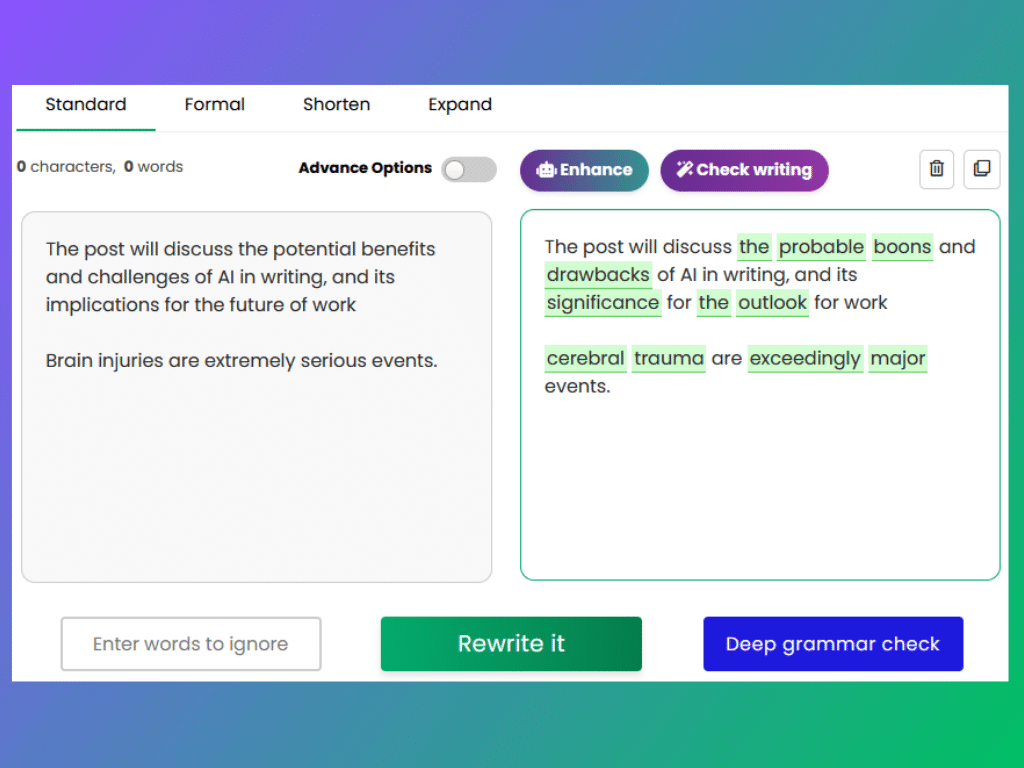
7. Change of Voice:
Changing the voice of a sentence (from active to passive or vice versa) is another form of paraphrasing. This can be particularly useful when you want to shift the focus of a sentence or avoid repetition. Consider this example:
Original Sentence: “Scientists made a groundbreaking discovery.”
Paraphrase (passive voice): “A groundbreaking discovery was made by scientists.”
8. Incorporating Quotations:
While not strictly paraphrasing, incorporating direct quotations from the original text is a way to use the author’s exact words while citing the source properly.
For example:
Original Text: According to Smith (2020), “Climate change is a pressing global issue.”
Paraphrase (with quotation): As Smith (2020) pointed out, “The issue of climate change is of utmost global concern.”
9. Expanding or Elaborating:
Sometimes, you may need to expand upon an idea presented in the original text. This involves adding more details or examples to provide a deeper understanding of the topic. For instance:
Original: “The research showed a correlation between sleep patterns and productivity.”
Expanded version: “The research findings indicated a strong correlation between individuals’ sleep patterns, including both duration and quality of sleep, and their overall productivity in various aspects of life, such as work and daily activities.”
10. Re-contextualization
This type of paraphrasing involves placing the ideas or information from the original text into a different context. It can help you see the information from a new perspective or adapt it for a different audience.
Example:
Original Context (medical journal): “The study demonstrated the effectiveness of the new drug in treating hypertension.”
Paraphrase (news article): “In a breakthrough discovery, a new medication has been shown to effectively combat high blood pressure, offering hope to millions of people seeking better treatments for hypertension.”
The choice of which type of paraphrasing to use depends on your purpose and the specific requirements of your writing or research. It’s essential to maintain the integrity of the original meaning while expressing it in your own words. Additionally, proper citation is crucial to prevent plagiarism when paraphrasing the work of others.
Other Helpful Resources: